
Integrations are what takes Slack from a normal online instant messaging and collaboration system to a solution that enables you to centralize all your notifications, from sales to tech support, social media and more, into one searchable place where your team can discuss and take action on each. In this article, I’ll share a simple bash script that reports local disk storage levels to Slack at a continuous time interval. It is easily deployable to multiple instances, highly configurable, and can helps teams take proactive measures in maintaining the operational well-being of their systems.
Download the App on GitHub
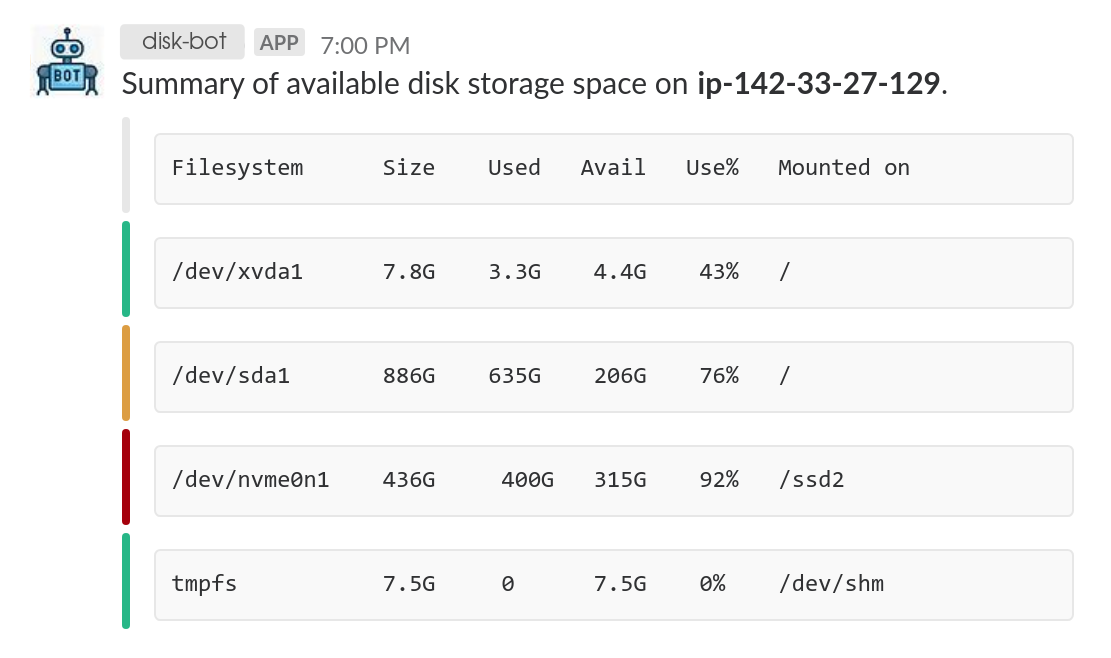
The script is available on GitHub and can be dropped anywhere on the instance you want to monitor. At a specified interval, it will
post disk storage related information to slack as illustrated above. The drive information is retrieved using the df -h command on Unix systems. Additionally, listed drives on the system are color coded based on how much
storage capacity they have left. Two quick steps are required for getting the integration setup and running.
1 - Create a Slack Webhook Notification:
This will allow the script to post as a bot/integration instead of as yourself (which would
require your personal credentials). First, ensure the Incoming WebHooks app
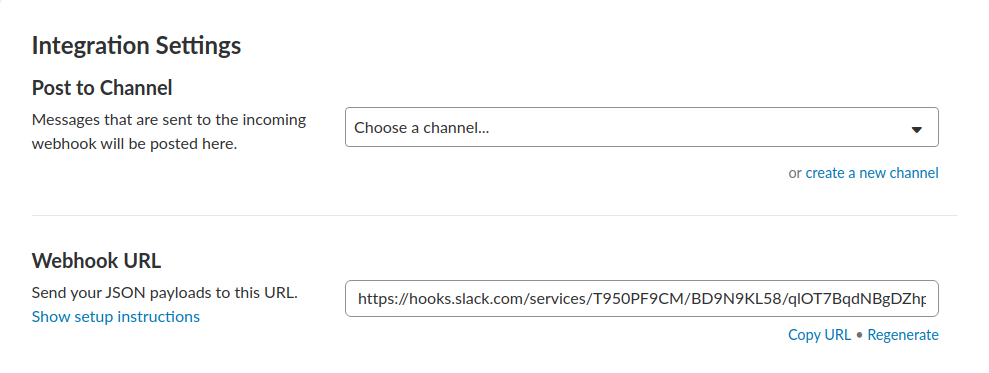
is installed in your slack organization. Next, click Add Configuration and read the instructions to configure the integration settings
as desired. Copy the value for the Webhook URL field, which will be required in the next step.
2 - Use a time-based job scheduler to run the script:
The job scheduler will execute the script regularly at a time interval based
on how often we want to view the reports. On a Linux environment, the crontab command, which is used to schedule
commands to be executed periodically, is the perfect tool for the job. To create a new cronjob, simply type crontab -e in a command
prompt. New jobs can be installed by adding a new entry to the file with the following syntax:
1 2 3 4 5 /path/to/command arg1 arg2
Where,
1 - Minute (0-59)
2 - Hours (0-23)
3 - Day (0-31)
4 - Month (0-12 [12 == December])
5 - Day of the week(0-7 [7 or 0 == sunday])
/path/to/command – Script or command name to schedule
To run the script, simply execute it as a bash script. The Webhook URL generated in step 1 can be inputted to the script either as the first agrument when executing the script or
as an environment variable named SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL. Assuming the Webhook URL is stored in this environment variable,
the script should be run every week at midnight on Sunday, and the script is located in my home folder,
the following crontab entry would do the trick:
* * * * 0 ./home/slack_storage_notifier.sh
Note the machine name used in the slack message corresponds the the $HOSTNAME environment variable on the instance. And that’s everything you need to get the integration working. Thank you for reading, please leave your comments and questions, and have a great day!
